Heat pipes can be made into almost any shape by bending and/or flattening, subject to certain parameters. The typical minimum bending radius is 3 times the diameter of the pipe. However, bending heat pipes reduces their Qmax, or maximum power transfer capacity. Smooth, gradual bending is less effective than tight bending, but a good rule of thumb is that Qmax will decrease by 2.5% for every 45 degree bend.
Flattening a sintered heat pipe to one-third of its original diameter is generally considered the maximum, although this number decreases with smaller pipes (2-4mm) and increases with larger pipes (>10mm). Ultra-thin heat pipes can be produced using other wick structures. When the pipe flattens, performance suffers. The figure below provides some insight into how flatness affects the performance of heat pipes. If the heat pipe is properly matched to the application, its Qmax is determined by the lower of the core limit or steam limit. For example, for a circular 6 mm standard heat pipe, the core limit (black dashed line) is just under 60 watts. Flattening it to 4, 3.5 or 3mm has no effect on its Qmax because the steam limit is higher than the wick limit. Note that flattening a circular 8 or 10mm heat pipe to 3mm or 2.5mm will have a significant impact on its Qmax.
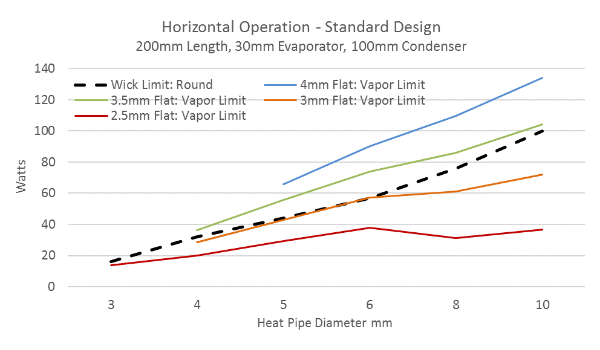
The maximum heat pipe carrying capacity is the lesser of the core limit and the steam limit
Heat pipe technology offers several advantages over other cooling mechanisms, including high thermal conductivity, ease of forming and bending, and long service life. Disadvantages include the higher cost of heat pipe equipment, especially compared to solid aluminum alternatives. Loop heat pipes, soaking plates, and oscillating heat pipes are alternative types of two-phase devices used to cool electronic devices, providing greater design flexibility and higher power handling capabilities in specific applications.
Heat pipes are particularly useful for improving radiator performance in applications where heat needs to be moved or diffused efficiently to the condenser area of the radiator, such as in low or no airflow conditions, or when the radiator is separated from the heat source. When designing heat pipes, engineers should carefully consider a range of factors, including operating temperature range, power density, thermal budget, size limitations, and mechanical requirements.
Jingshengxin Technology (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. is a custom radiator manufacturer of heat pipe technology.
We focus on: radiator design, radiator prototype, radiator manufacturing, heat pipe and other materials.